Hi everyone,
I am currently working on a medical image processing task that involves the registration of five CT image series for a single patient. My dataset consists of:
One CT scan acquired during an External Radiotherapy (EBRT) session, which presents a significantly different Field of View compared to the others and four subsequent CT scans from Brachytherapy for the cervix.
To continue my work, a crucial pre-processing step is required:
- Homogenizing the spatial information (Origin, Image Spacing, and FOV) across all five images to ensure they reside in a consistent physical space.
- Extracting the largest common anatomical region that is present in all scans, to serve as the input for subsequent registration and analysis steps.
I have been exploring the SimpleITK-Notebooks for guidance, particularly the “Create reference domain” section in:
(SimpleITK-Notebooks/Python/70_Data_Augmentation.ipynb at main · InsightSoftwareConsortium/SimpleITK-Notebooks · GitHub) to define a unified image space.
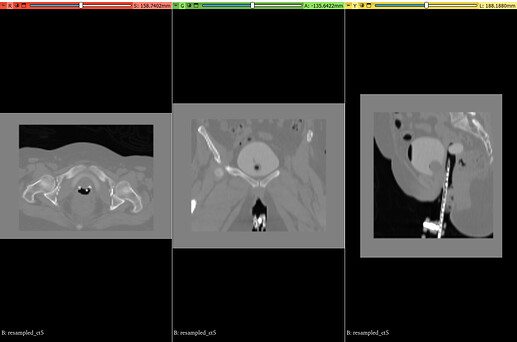
Despite this, I am consistently encountering persistent and undesirable padding in various anatomical views (axial, sagittal, and coronal) of the processed images. Furthermore, some of my attempts have resulted in excessive cropping, inadvertently removing valuable anatomical structures required for downstream analysis.
Could you please provide guidance on how to robustly achieve a clean, common anatomical region across all these diverse CT scans, ensuring no residual padding remains while preserving essential anatomical features (like applicators or the bladder) and avoiding over-cropping?
Thanks a lot
my code:
import SimpleITK as sitk
import numpy as np
import os
def read_dicom_series(directory):
“”"
Reads a DICOM series from a directory and returns a SimpleITK Image object.
“”"
if not os.path.isdir(directory):
raise FileNotFoundError(f"Directory not found: {directory}“)
series_IDs = sitk.ImageSeriesReader.GetGDCMSeriesIDs(directory)
if not series_IDs:
raise ValueError(f"No DICOM series found in directory: {directory}”)
series_files = sitk.ImageSeriesReader.GetGDCMSeriesFileNames(directory, series_IDs[0])
reader = sitk.ImageSeriesReader()
reader.SetFileNames(series_files)
image = reader.Execute()
print(f"Loaded DICOM series from {directory} with size {image.GetSize()}, origin {image.GetOrigin()}, spacing {image.GetSpacing()}“)
return image
def compute_physical_bounds(img):
“””
Computes the physical bounds (min and max coordinates) of an image in physical space.
Returns a tuple of (min_bounds, max_bounds) for each dimension.
“”"
size = np.array(img.GetSize())
spacing = np.array(img.GetSpacing())
origin = np.array(img.GetOrigin())
max_bounds = origin + (size - 1) * spacing
return origin, max_bounds
def crop_to_common_region(images):
“”"
Crops all images to the common anatomical region (intersection of physical bounds).
Returns a list of cropped images.
“”"
if not images:
raise ValueError(“No images provided for cropping.”)
# Computes physical bounds for all images
bounds = [compute_physical_bounds(img) for img in images]
min_bounds_all = [b[0] for b in bounds] # List of origins
max_bounds_all = [b[1] for b in bounds] # List of max coordinates
# FindS the common region (max of min bounds, min of max bounds)
common_min = np.max(min_bounds_all, axis=0)
common_max = np.min(max_bounds_all, axis=0)
if np.any(common_min >= common_max):
print(“Warning: No common region found among the images. Returning original images.”)
return images
print(f"Common physical region for cropping: Min bounds {common_min}, Max bounds {common_max}“)
# Crops each image to the common region
cropped_images = [ ]
for i, img in enumerate(images):
origin = np.array(img.GetOrigin())
spacing = np.array(img.GetSpacing())
size = np.array(img.GetSize())
# Compute index bounds for cropping
start_idx = np.maximum(0, np.ceil((common_min - origin) / spacing)).astype(int)
end_idx = np.minimum(size, np.floor((common_max - origin) / spacing) + 1).astype(int)
if np.any(end_idx <= start_idx):
print(f"Warning: Cannot crop image {i+1} (invalid bounds {start_idx} to {end_idx}). Keeping original.”)
cropped_images.append(img)
continue
# Extract region
cropped_img = img[start_idx[0]:end_idx[0], start_idx[1]:end_idx[1], start_idx[2]:end_idx[2]]
print(f"Cropped image {i+1} to size {cropped_img.GetSize()}“)
cropped_images.append(cropped_img)
return cropped_images
def create_reference_domain(images, pixel_size_per_dimension=128):
“””
Uses the largest physical size among images.
“”"
dimension = images[0].GetDimension()
# Computes the largest physical size among all images
reference_physical_size = np.zeros(dimension)
for img in images:
phys_size = np.array([(sz - 1) * spc for sz, spc in zip(img.GetSize(), img.GetSpacing())])
reference_physical_size = np.maximum(reference_physical_size, phys_size)
print(f"Reference physical size (largest FOV): {reference_physical_size}“)
# Sets origin and direction to standard values (as in the notebook)
reference_origin = np.zeros(dimension)
reference_direction = np.identity(dimension).flatten()
# Sets arbitrary pixel size
reference_size = [pixel_size_per_dimension] * dimension
reference_spacing = [phys_sz / (sz - 1) for sz, phys_sz in zip(reference_size, reference_physical_size)]
print(f"Reference size: {reference_size}”)
print(f"Reference spacing: {reference_spacing}“)
# Creates reference image
reference_image = sitk.Image(reference_size, images[0].GetPixelIDValue())
reference_image.SetOrigin(reference_origin)
reference_image.SetSpacing(reference_spacing)
reference_image.SetDirection(reference_direction)
# Computes reference center (as in the notebook)
reference_center = np.array(
reference_image.TransformContinuousIndexToPhysicalPoint(
np.array(reference_image.GetSize()) / 2.0
)
)
print(f"Reference center: {reference_center}”)
return reference_image
def resample_to_reference(images, reference_image):
“”"
Resamples all images to the reference domain, centering them.
“”"
resampled_images = [ ]
for i, img in enumerate(images):
# Creates a transform to center the image in the reference domain
transform = sitk.CenteredTransformInitializer(
reference_image,
img,
sitk.Euler3DTransform(),
sitk.CenteredTransformInitializerFilter.GEOMETRY
)
resampler = sitk.ResampleImageFilter()
resampler.SetReferenceImage(reference_image)
resampler.SetInterpolator(sitk.sitkBSpline)
resampler.SetTransform(transform)
resampler.SetDefaultPixelValue(0)
resampled_img = resampler.Execute(img)
print(f"Resampled image {i+1} to reference domain with size {resampled_img.GetSize()}“)
resampled_images.append(resampled_img)
return resampled_images
dicom_dirs = [
r’C:\Users\Desktop\extrenal’,
r’C:\Users\Desktop\fr1’,
r’C:\Users\Desktop\fr2’,
r’C:\Users\Desktop\fr3’,
r’C:\Users\Desktop\fr4’
]
output_dir = r’C:\Users\Desktop\resampled’
if not os.path.exists(output_dir):
os.makedirs(output_dir)
# Step 1: Loads DICOM series
images = [read_dicom_series(dir_path) for dir_path in dicom_dirs]
# Step 2: Crops to common region (to preserve only the intersection of physical regions)
do_crop_to_common = True
if do_crop_to_common:
processed_images = crop_to_common_region(images)
else:
processed_images = images
print(“Skipping cropping to common region; using original images directly.”)
# Step 3: Creates reference domain (using largest physical size)
reference_image = create_reference_domain(processed_images, pixel_size_per_dimension=128)
# Step 4: Resamples all images to reference domain with centering
resampled_images = resample_to_reference(processed_images, reference_image)
# Step 5: Saves resampled images (as NIfTI)
for i, resampled_img in enumerate(resampled_images):
output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, f’resampled_ct{i+1}.nii’)
sitk.WriteImage(resampled_img, output_path)
print(f"Saved resampled image to {output_path}”)