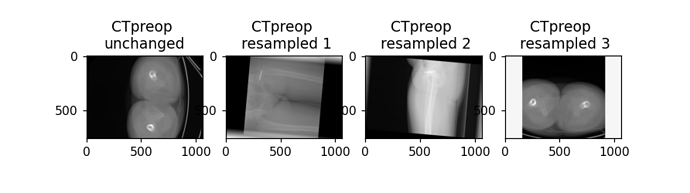
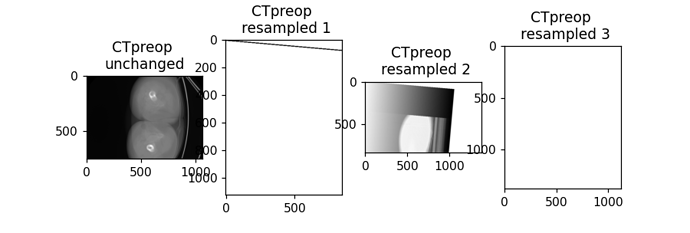
Hi there,
I’m trying to rotate a 3D volume using the Euler3D transform. For this, I first used the code below, but I found that the image size does not change if the image is rotated, which is explainable since I use input image as a reference image. However, I do want the image size to change since it sometimes results in not seeing the entire rotated image, so I edited the resampling code from the simpleITK notebooks in such a way that I would think it should work. However, I do not get good results and I don’t know what I’m doing wrong.
Could anybody help me with this?
Thank you!
Images:
Code first try:
def make_isotropic(image, interpolator = sitk.sitkLinear, spacing = None):
'''
Many file formats (e.g. jpg, png,...) expect the pixels to be isotropic, same
spacing for all axes. Saving non-isotropic data in these formats will result in
distorted images. This function makes an image isotropic via resampling, if needed.
Args:
image (SimpleITK.Image): Input image.
interpolator: By default the function uses a linear interpolator. For
label images one should use the sitkNearestNeighbor interpolator
so as not to introduce non-existant labels.
spacing (float): Desired spacing. If none given then use the smallest spacing from
the original image.
Returns:
SimpleITK.Image with isotropic spacing which occupies the same region in space as
the input image.
'''
original_spacing = image.GetSpacing()
# Image is already isotropic, just return a copy.
if all(spc == original_spacing[0] for spc in original_spacing):
return sitk.Image(image)
# Make image isotropic via resampling.
original_size = image.GetSize()
if spacing is None:
spacing = min(original_spacing)
new_spacing = [spacing]*image.GetDimension()
new_size = [int(round(osz*ospc/spacing)) for osz,ospc in zip(original_size, original_spacing)]
return sitk.Resample(image, new_size, sitk.Transform(), interpolator,
image.GetOrigin(), new_spacing, image.GetDirection(), 0,
image.GetPixelID())
# Load image
filename_CTpreop = 'ctpreop.mha'
CTpreop = sitk.ReadImage(filename_CTpreop)
CTpreop_iso = make_isotropic(CTpreop)
CTpreop_np = sitk.GetArrayFromImage(CTpreop)
CTpreop_iso_np = sitk.GetArrayFromImage(CTpreop_iso)
# This function is from https://github.com/rock-learning/pytransform3d/blob/7589e083a50597a75b12d745ebacaa7cc056cfbd/pytransform3d/rotations.py#L302
def matrix_from_angle(basis, angle):
"""Compute rotation matrix from rotation around basis vector.
The combined rotation matrices are either extrinsic and can be used with
pre-multiplied column vectors or they are intrinsic and can be used with
post-multiplied row vectors. We use a right-hand system with right-hand
rotations. We use the passive / alias convention. You can derive the
active / alibi rotation matrix by transposing the rotation matrix.
Parameters
----------
basis : int from [0, 1, 2]
The rotation axis (0: x, 1: y, 2: z)
angle : float
Rotation angle
Returns
-------
R : array-like, shape (3, 3)
Rotation matrix
"""
c = np.cos(angle)
s = np.sin(angle)
if basis == 0:
R = np.array([[1.0, 0.0, 0.0],
[0.0, c, s],
[0.0, -s, c]])
elif basis == 1:
R = np.array([[c, 0.0, -s],
[0.0, 1.0, 0.0],
[s, 0.0, c]])
elif basis == 2:
R = np.array([[c, s, 0.0],
[-s, c, 0.0],
[0.0, 0.0, 1.0]])
else:
raise ValueError("Basis must be in [0, 1, 2]")
return R
def matrix_from_euler_xyz(e):
"""Compute rotation matrix from xyz Euler angles.
Intrinsic rotations are used to create the transformation matrix
from three concatenated rotations.
The xyz convention is usually used in physics and chemistry.
Parameters
----------
e : array-like, shape (3,)
Angles for rotation around x-, y'-, and z''-axes (intrinsic rotations)
Returns
-------
R : array-like, shape (3, 3)
Rotation matrix
"""
alpha, beta, gamma = e
# We use intrinsic rotations
Qx = matrix_from_angle(0, alpha)
Qy = matrix_from_angle(1, beta)
Qz = matrix_from_angle(2, gamma)
R = Qx.dot(Qy).dot(Qz)
return R
def resample(image, transform):
"""
This function resamples (updates) an image using a specified transform
:param image: The sitk image we are trying to transform
:param transform: An sitk transform (ex. resizing, rotation, etc.
:return: The transformed sitk image
"""
reference_image = image
interpolator = sitk.sitkLinear
default_value = 0
return sitk.Resample(image, reference_image, transform,
interpolator, default_value)
def get_center(img):
"""
This function returns the physical center point of a 3d sitk image
:param img: The sitk image we are trying to find the center of
:return: The physical center point of the image
"""
width, height, depth = img.GetSize()
return img.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((int(np.ceil(width/2)),
int(np.ceil(height/2)),
int(np.ceil(depth/2))))
def rotation3d(image, theta_x, theta_y, theta_z):
"""
This function rotates an image across each of the x, y, z axes by theta_x, theta_y, and theta_z degrees
respectively
:param image: An sitk 3D image
:param theta_x: The amount of degrees the user wants the image rotated around the x axis
:param theta_y: The amount of degrees the user wants the image rotated around the y axis
:param theta_z: The amount of degrees the user wants the image rotated around the z axis
:param show: Boolean, whether or not the user wants to see the result of the rotation
:return: The rotated image
"""
euler_transform = sitk.Euler3DTransform()
image_center = get_center(image)
euler_transform.SetCenter(image_center)
#theta_x = np.deg2rad(theta_x)
#theta_y = np.deg2rad(theta_y)
#theta_z = np.deg2rad(theta_z)
euler_angles = theta_x, theta_y, theta_z
rot_mat_euler = matrix_from_euler_xyz(euler_angles)
euler_transform.SetMatrix(rot_mat_euler.flatten().tolist())
resampled_image = resample(image, euler_transform)
return resampled_image
projection= CTpreop_iso_np.sum(axis=1)
[theta_x, theta_y, theta_z] = 0.5*np.pi, 0 , 0
resampled_image1 = make_isotropic(rotation3d(CTpreop, theta_x,theta_y, theta_z))
[theta_x, theta_y, theta_z] = 0, 0.5*np.pi, 0
resampled_image2 = make_isotropic(rotation3d(CTpreop, theta_x,theta_y, theta_z))
[theta_x, theta_y, theta_z] = 0, 0, 0.5*np.pi
resampled_image3 = make_isotropic(rotation3d(CTpreop, theta_x,theta_y, theta_z))
resampled_image1_np = sitk.GetArrayViewFromImage(resampled_image1)
resampledprojection1 = resampled_image1_np.sum(axis=1)
resampled_image2_np = sitk.GetArrayViewFromImage(resampled_image2)
resampledprojection2 = resampled_image2_np.sum(axis=1)
resampled_image3_np = sitk.GetArrayViewFromImage(resampled_image3)
resampledprojection3 = resampled_image3_np.sum(axis=1)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, 1)
imgplot = plt.imshow(projection, cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('CTpreop \nunchanged')
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, 2)
imgplot = plt.imshow(resampledprojection1, cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('CTpreop \n resampled 1')
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, 3)
imgplot = plt.imshow(resampledprojection2, cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('CTpreop \n resampled 2')
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 4, 4)
imgplot = plt.imshow(resampledprojection3, cmap='gray')
ax.set_title('CTpreop \n resampled 3')
After that I changed the resample and rotation3d function like this:
def resample(image, transform, output_size, output_origin, output_spacing, output_direction):
"""
This function resamples (updates) an image using a specified transform
:param image: The sitk image we are trying to transform
:param transform: An sitk transform (ex. resizing, rotation, etc.
:return: The transformed sitk image
"""
interpolator = sitk.sitkLinear
default_value = 0
return sitk.Resample(image,output_size, transform,
interpolator, output_origin, output_spacing, output_direction)
def rotation3d(image, theta_x, theta_y, theta_z):
"""
This function rotates an image across each of the x, y, z axes by theta_x, theta_y, and theta_z degrees
respectively
:param image: An sitk 3D image
:param theta_x: The amount of degrees the user wants the image rotated around the x axis
:param theta_y: The amount of degrees the user wants the image rotated around the y axis
:param theta_z: The amount of degrees the user wants the image rotated around the z axis
:param show: Boolean, whether or not the user wants to see the result of the rotation
:return: The rotated image
"""
euler_transform = sitk.Euler3DTransform()
image_center = get_center(image)
euler_transform.SetCenter(image_center)
#theta_x = np.deg2rad(theta_x)
#theta_y = np.deg2rad(theta_y)
#theta_z = np.deg2rad(theta_z)
euler_angles = theta_x, theta_y, theta_z
rot_mat_euler = matrix_from_euler_xyz(euler_angles)
euler_transform.SetMatrix(rot_mat_euler.flatten().tolist())
extreme_points = [image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((0,0,0)),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((image.GetWidth(),0,0)),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((image.GetWidth(),0,image.GetDepth())),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((image.GetWidth(),image.GetHeight(),0)),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((image.GetWidth(),image.GetHeight(),image.GetDepth())),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((0,image.GetHeight(), 0)),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((0,image.GetHeight(), image.GetDepth())),
image.TransformIndexToPhysicalPoint((0,0, image.GetDepth()))]
inv_euler3d = euler_transform.GetInverse()
extreme_points_transformed = [inv_euler3d.TransformPoint(pnt) for pnt in extreme_points]
min_x = min(extreme_points_transformed)[0]
min_y = min(extreme_points_transformed, key=lambda p: p[1])[1]
min_z = min(extreme_points_transformed, key=lambda p: p[2])[2]
max_x = max(extreme_points_transformed)[0]
max_y = max(extreme_points_transformed, key=lambda p: p[1])[1]
max_z = max(extreme_points_transformed, key=lambda p: p[2])[2]
output_spacing = image.GetSpacing()
output_size = [int((max_x-min_x)/output_spacing[0]), int((max_y-min_y)/output_spacing[1]), int((max_z-min_z)/output_spacing[2])]
print(output_size)
input_origin = image.GetOrigin()
output_origin = inv_euler3d.TransformPoint(input_origin)
output_direction = image.GetDirection()
resampled_image = resample(image, euler_transform, output_size, output_origin, output_spacing, output_direction)
return resampled_image