Hello everyone,
I have two CT images that I want to register together. One is from external beam radiotherapy (EBRT), and the other is from brachytherapy. Before registration, I harmonized both images by making their Origin, dimensions, Spacing, and etc. identical. Additionally, I modified the Hounsfield units of the bladder and rectum in both images. Since the applicator is not present in the EBRT image, I set its Hounsfield unit to zero in the brachytherapy image.
After that, I ran the following code for registration. In writing parts of this code, I also drew from examples in the link: Examples — SimpleITK 2.4.0 documentation.
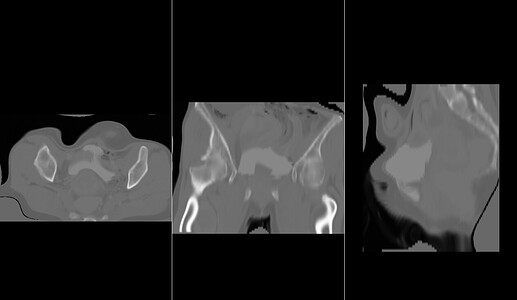
However, despite the long execution time, I didn’t achieve good results. here is my result image. As you can see in the image, the registered image is not satisfactory.
Can you guide me on how to register two CT images with significant changes in organs like the bladder and rectum, so that I can achieve good accuracy without the process taking too long?
Thanks a lot
Here is my code:
import SimpleITK as sitk
import os
import time
import gc
sitk.ProcessObject.SetGlobalDefaultNumberOfThreads(0)
def read_dicom_series(directory):
print(f"Loading DICOM series from: {directory}“)
series_IDs = sitk.ImageSeriesReader.GetGDCMSeriesIDs(directory)
if not series_IDs:
raise ValueError(f"No DICOM series found in directory: {directory}”)
series_files = sitk.ImageSeriesReader.GetGDCMSeriesFileNames(directory, series_IDs[0])
reader = sitk.ImageSeriesReader()
reader.SetFileNames(series_files)
image = reader.Execute()
return sitk.Cast(image, sitk.sitkFloat32)
#Configuration
fixed_ct_dir = r’D:\fr1\CT_Unified’
moving_ct_dir = r’D:\extr\CT_Unified’
output_dir = r’D:\registration_output’
#Main Script
os.makedirs(output_dir, exist_ok=True)
dvf_output_path = os.path.join(output_dir, ‘final_dvf_extr_to_fr1.mha’)
resampled_moving_ct_path = os.path.join(output_dir, ‘resampled_moving_ct.nii.gz’)
total_start_time = time.time()
fixed_image = read_dicom_series(fixed_ct_dir)
moving_image = read_dicom_series(moving_ct_dir)
print(f"Images loaded successfully. Fixed image size: {fixed_image.GetSize()}“)
sampling_percentage = 0.05
#Stages 1 & 2: Rigid and Affine
print(”\n— Starting Stage 1: Rigid Registration —“)
R_rigid = sitk.ImageRegistrationMethod()
R_rigid.SetMetricAsMattesMutualInformation(numberOfHistogramBins=50)
R_rigid.SetMetricSamplingStrategy(R_rigid.RANDOM)
R_rigid.SetMetricSamplingPercentage(sampling_percentage)
R_rigid.SetInterpolator(sitk.sitkLinear)
R_rigid.SetOptimizerAsGradientDescent(learningRate=1.0, numberOfIterations=200, convergenceMinimumValue=1e-6, convergenceWindowSize=20)
R_rigid.SetOptimizerScalesFromPhysicalShift()
R_rigid.SetShrinkFactorsPerLevel(shrinkFactors=[8, 4, 2])
R_rigid.SetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel(smoothingSigmas=[4, 2, 1])
R_rigid.SmoothingSigmasAreSpecifiedInPhysicalUnitsOn()
initial_rigid_transform = sitk.CenteredTransformInitializer(fixed_image, moving_image, sitk.Euler3DTransform(), sitk.CenteredTransformInitializerFilter.GEOMETRY)
R_rigid.SetInitialTransform(initial_rigid_transform)
rigid_transform = R_rigid.Execute(fixed_image, moving_image)
print(f"Rigid registration finished. Final Metric: {R_rigid.GetMetricValue():.4f}”)
print(“\n— Starting Stage 2: Affine Registration —”)
R_affine = sitk.ImageRegistrationMethod()
R_affine.SetMetricAsMattesMutualInformation(numberOfHistogramBins=50)
R_affine.SetMetricSamplingStrategy(R_affine.RANDOM)
R_affine.SetMetricSamplingPercentage(sampling_percentage)
R_affine.SetInterpolator(sitk.sitkLinear)
R_affine.SetOptimizerAsGradientDescent(learningRate=1.0, numberOfIterations=200, convergenceMinimumValue=1e-6, convergenceWindowSize=20)
R_affine.SetOptimizerScalesFromPhysicalShift()
R_affine.SetShrinkFactorsPerLevel(shrinkFactors=[4, 2])
R_affine.SetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel(smoothingSigmas=[2, 1])
R_affine.SmoothingSigmasAreSpecifiedInPhysicalUnitsOn()
initial_affine_transform = sitk.AffineTransform(3)
initial_affine_transform.SetMatrix(rigid_transform.GetMatrix())
initial_affine_transform.SetTranslation(rigid_transform.GetTranslation())
initial_affine_transform.SetCenter(rigid_transform.GetCenter())
R_affine.SetInitialTransform(initial_affine_transform)
affine_transform = R_affine.Execute(fixed_image, moving_image)
print(f"Affine registration finished. Final Metric: {R_affine.GetMetricValue():.4f}“)
#Stage 3: Multi-level B-Spline Registration
print(”\n— Starting Stage 3: Multi-Level B-Spline Registration —“)
moving_prealigned = sitk.Resample(moving_image, fixed_image, affine_transform, sitk.sitkLinear, 0.0, moving_image.GetPixelID())
#B-Spline Coarse Stage
print(”— Sub-stage: Coarse B-Spline —“)
R_bspline_coarse = sitk.ImageRegistrationMethod()
R_bspline_coarse.SetMetricAsMattesMutualInformation(numberOfHistogramBins=50)
R_bspline_coarse.SetMetricSamplingStrategy(R_bspline_coarse.RANDOM)
R_bspline_coarse.SetMetricSamplingPercentage(sampling_percentage)
R_bspline_coarse.SetInterpolator(sitk.sitkLinear)
R_bspline_coarse.SetOptimizerAsLBFGSB(gradientConvergenceTolerance=1e-5, numberOfIterations=100, maximumNumberOfCorrections=5)
transform_domain_mesh_size_coarse = [10] * fixed_image.GetDimension()
R_bspline_coarse.SetInitialTransform(sitk.BSplineTransformInitializer(image1=fixed_image, transformDomainMeshSize=transform_domain_mesh_size_coarse))
R_bspline_coarse.SetShrinkFactorsPerLevel([4, 2])
R_bspline_coarse.SetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel([2, 1])
bspline_transform_coarse = R_bspline_coarse.Execute(fixed_image, moving_prealigned)
print(f"B-Spline (Coarse) finished. Metric: {R_bspline_coarse.GetMetricValue():.4f}”)
#B-Spline Fine Stage
print(“— Sub-stage: Fine B-Spline —”)
R_bspline_fine = sitk.ImageRegistrationMethod()
R_bspline_fine.SetMetricAsANTSNeighborhoodCorrelation(radius=5)
R_bspline_fine.SetMetricSamplingStrategy(R_bspline_fine.RANDOM)
R_bspline_fine.SetMetricSamplingPercentage(sampling_percentage)
R_bspline_fine.SetInterpolator(sitk.sitkLinear)
R_bspline_fine.SetOptimizerAsLBFGSB(gradientConvergenceTolerance=1e-5, numberOfIterations=100, maximumNumberOfCorrections=5)
transform_domain_mesh_size_fine = [12] * fixed_image.GetDimension()
R_bspline_fine.SetInitialTransform(bspline_transform_coarse, inPlace=False)
R_bspline_fine.SetShrinkFactorsPerLevel([2, 1])
R_bspline_fine.SetSmoothingSigmasPerLevel([1, 0])
bspline_transform_fine = R_bspline_fine.Execute(fixed_image, moving_prealigned)
print(f"B-Spline (Fine) finished. Final Metric: {R_bspline_fine.GetMetricValue():.4f}“)
#Final Stage: Combine and Save
print(”\n— Final Stage: Combining transforms and generating DVF —“)
final_transform = sitk.CompositeTransform(affine_transform)
final_transform.AddTransform(bspline_transform_fine)
displacement_filter = sitk.TransformToDisplacementFieldFilter()
displacement_filter.SetReferenceImage(fixed_image)
final_dvf = displacement_filter.Execute(final_transform)
final_dvf = sitk.Cast(final_dvf, sitk.sitkVectorFloat64)
print(“Clearing intermediate objects from memory…”)
del R_rigid, R_affine, R_bspline_coarse, R_bspline_fine, rigid_transform, affine_transform, bspline_transform_coarse, bspline_transform_fine, moving_prealigned, final_transform, displacement_filter
gc.collect()
print(“Writing final DVF…”)
sitk.WriteImage(final_dvf, dvf_output_path)
print(f"Final DVF saved to: {dvf_output_path}”)
print(“\n— Generating resampled CT —”)
dvf_transform = sitk.DisplacementFieldTransform(final_dvf)
resampled_moving = sitk.Resample(moving_image, fixed_image, dvf_transform, sitk.sitkLinear, 0.0)
sitk.WriteImage(resampled_moving, resampled_moving_ct_path)
print(f"Final resampled moving CT (for validation) saved to: {resampled_moving_ct_path}“)
print(f”\nRegistration completed successfully in {time.time() - total_start_time:.2f} seconds.")