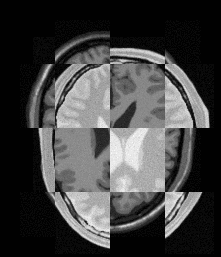
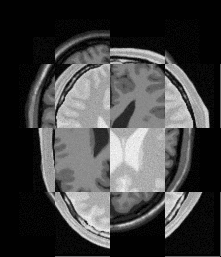
The result seems very unsatisfactory,and my weight adjustment has no effect on the result
You might need to increase optimizer’s initial step size, allow for more iterations, have a better initialization, etc. Achieving that with a more complicated setup (multi-metric) is harder than with a simpler setup (e.g. mutual information metric). Try to make it work with a simpler setup before making it more complicated. To presumably make it work for larger variety of cases?
That looks like the initial location is poor and a large distance needs to be traveled by the registration optimization.
Consider removed the high frequencies with smoothing and using a multi-scale/resolution approach.
I feel I’m a little off track. What I need to do is 2D-3D multimodal registration of blood vessels. I wanted to find a good metric for 2D-3D registration from 2D-2D multimodal registration.The effect of 2d-3d registration is very bad. My code is as follows:
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
double projAngle1 =0.;
// Default output file names
const char* fileOutput1 = "out_put.tif";
bool ok;
bool verbose = true;
bool debug = false;
bool customized_iso = false;
bool customized_2DCX = false; // Flag for customized 2D image central axis positions
bool customized_2DRES = true; // Flag for customized 2D image pixel spacing
double rx = 0.;
double ry = 0.;
double rz = 0.;
double tx = -5.;
double ty = 0.;
double tz = -5.;
double cx = 0.;
double cy = 0.;
double cz = 0.;
double scd = 1061.; // Source to isocenter distance
double image1centerX = 0.0;
double image1centerY = 0.0;
double image1resX = 0.37;
double image1resY = 0.37;
double threshold = 0.0;
constexpr unsigned int Dimension = 3;
using InternalPixelType = float;
using PixelType3D = short;
using ImageType3D = itk::Image<PixelType3D, Dimension>;
using OutputPixelType = unsigned char;
using OutputImageType = itk::Image<OutputPixelType, Dimension>;
// The following lines define each of the components used in the
// registration: The transform, optimizer, metric, interpolator and
// the registration method itself.
using InternalImageType = itk::Image<InternalPixelType, Dimension>;
using TransformType = itk::Euler3DTransform<double>;
/*using TransformType = itk::Rigid3DTransform<double>;*/
using OptimizerType = itk::PowellOptimizer;
/*using MetricType = itk::NormalizedCorrelationImageToImageMetric<InternalImageType, InternalImageType>;*/
using MetricType = itk::MutualInformationImageToImageMetric<InternalImageType, InternalImageType>;
/*using MetricType = itk::GradientDifferenceImageToImageMetric<InternalImageType, InternalImageType>;*/
using InterpolatorType = itk::SiddonJacobsRayCastInterpolateImageFunction<InternalImageType, double>;
using RegistrationType = itk::ImageRegistrationMethod<InternalImageType, InternalImageType>;
MetricType::Pointer metric = MetricType::New();
TransformType::Pointer transform = TransformType::New();
OptimizerType::Pointer optimizer = OptimizerType::New();
InterpolatorType::Pointer interpolator1 = InterpolatorType::New();
RegistrationType::Pointer registration = RegistrationType::New();
metric->ComputeGradientOff();
/* metric->ComputeGradientOn();*/
/* metric->SetSubtractMean(false);*/
registration->SetMetric(metric);
registration->SetOptimizer(optimizer);
registration->SetTransform(transform);
registration->SetInterpolator(interpolator1);
metric->SetFixedImageStandardDeviation(0.4);
metric->SetMovingImageStandardDeviation(0.4);
using ImageReaderType2D = itk::ImageFileReader<InternalImageType>;
using ImageReaderType3D = itk::ImageFileReader<ImageType3D>;
using ImageIOTypeNII = itk::NiftiImageIO;
ImageIOTypeNII::Pointer NiiImageIO = ImageIOTypeNII::New();
ImageReaderType2D::Pointer imageReader2D = ImageReaderType2D::New();
ImageReaderType3D::Pointer imageReader3D = ImageReaderType3D::New();
imageReader3D->SetImageIO(NiiImageIO);
imageReader2D->SetFileName("fixed_1.tif");
imageReader3D->SetFileName("ves_1.nii");
imageReader3D->Update();
ImageType3D::Pointer image3DIn = imageReader3D->GetOutput();
// To simply Siddon-Jacob's fast ray-tracing algorithm, we force the origin of the CT image
// to be (0,0,0). Because we align the CT isocenter with the central axis, the projection
// geometry is fully defined. The origin of the CT image becomes irrelavent.
//为了简化Siddon Jacob的快速光线跟踪算法,我们强制CT图像的原点为(0,0,0)。因为我们将CT等中心与中心轴对齐,
//所以投影几何体已完全定义。CT图像的来源变得无关
ImageType3D::PointType image3DOrigin;
image3DOrigin[0] = 0.0;
image3DOrigin[1] = 0.0;
image3DOrigin[2] = 0.0;
image3DIn->SetOrigin(image3DOrigin);
InternalImageType::Pointer image_tmp1 = imageReader2D->GetOutput();
imageReader2D->Update();
if (customized_2DRES)
{
InternalImageType::SpacingType spacing;
spacing[0] = image1resX;
spacing[1] = image1resY;
spacing[2] = 1.0;
image_tmp1->SetSpacing(spacing);
}
// The input 2D images were loaded as 3D images. They were considered
// as a single slice from a 3D volume. By default, images stored on the
// disk are treated as if they have RAI orientation. After view point
// transformation, the order of 2D image pixel reading is equivalent to
// from inferior to superior. This is contradictory to the traditional
// 2D x-ray image storage, in which a typical 2D image reader reads and
// writes images from superior to inferior. Thus the loaded 2D DICOM
// images should be flipped in y-direction. This was done by using a.
// FilpImageFilter.
using FlipFilterType = itk::FlipImageFilter<InternalImageType>;
FlipFilterType::Pointer flipFilter1 = FlipFilterType::New();
using FlipAxesArrayType = FlipFilterType::FlipAxesArrayType;
FlipAxesArrayType flipArray;
flipArray[0] = false;
flipArray[1] = true;
flipArray[2] = false;
flipFilter1->SetFlipAxes(flipArray);
flipFilter1->SetInput(imageReader2D->GetOutput());
// The input 2D images may have 16 bits. We rescale the pixel value to between 0-255.
using Input2DRescaleFilterType = itk::RescaleIntensityImageFilter<InternalImageType, InternalImageType>;
Input2DRescaleFilterType::Pointer rescaler2D1 = Input2DRescaleFilterType::New();
rescaler2D1->SetOutputMinimum(0);
rescaler2D1->SetOutputMaximum(255);
rescaler2D1->SetInput(flipFilter1->GetOutput());
// The 3D CT dataset is casted to the internal image type using
// {CastImageFilters}.
using CastFilterType3D = itk::CastImageFilter<ImageType3D, InternalImageType>;
CastFilterType3D::Pointer caster3D = CastFilterType3D::New();
caster3D->SetInput(image3DIn);
rescaler2D1->Update();
caster3D->Update();
registration->SetFixedImage(rescaler2D1->GetOutput());
registration->SetMovingImage(caster3D->GetOutput());
// Initialise the transform
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// Set the order of the computation. Default ZXY
transform->SetComputeZYX(true);
// The transform is initialised with the translation [tx,ty,tz] and
// rotation [rx,ry,rz] specified on the command line
TransformType::OutputVectorType translation;
translation[0] = tx;
translation[1] = ty;
translation[2] = tz;
transform->SetTranslation(translation);
// constant for converting degrees to radians
const double dtr = (atan(1.0) * 4.0) / 180.0;
transform->SetRotation(dtr * rx, dtr * ry, dtr * rz);
// The centre of rotation is set by default to the centre of the 3D
// volume but can be offset from this position using a command
// line specified translation [cx,cy,cz]
//旋转中心默认设置为 3D 体积的中心,但可以使用命令行指定的平移 [cx,cy,cz] 从此位置偏移
ImageType3D::PointType origin3D = image3DIn->GetOrigin();
const itk::Vector<double, 3> resolution3D = image3DIn->GetSpacing();
using ImageRegionType3D = ImageType3D::RegionType;
using SizeType3D = ImageRegionType3D::SizeType;
ImageRegionType3D region3D = caster3D->GetOutput()->GetBufferedRegion();
SizeType3D size3D = region3D.GetSize();
TransformType::InputPointType isocenter;
if (customized_iso)
{
// Isocenter location given by the user.
isocenter[0] = origin3D[0] + resolution3D[0] * cx;
isocenter[1] = origin3D[1] + resolution3D[1] * cy;
isocenter[2] = origin3D[2] + resolution3D[2] * cz;
}
else
{
// Set the center of the image as the isocenter.
isocenter[0] = origin3D[0] + resolution3D[0] * static_cast<double>(size3D[0]) / 2.0;
isocenter[1] = origin3D[1] + resolution3D[1] * static_cast<double>(size3D[1]) / 2.0;
isocenter[2] = origin3D[2] + resolution3D[2] * static_cast<double>(size3D[2]) / 2.0;
}
transform->SetCenter(isocenter);
if (verbose)
{
std::cout << "3D image size: " << size3D[0] << ", " << size3D[1] << ", " << size3D[2] << std::endl
<< " resolution: " << resolution3D[0] << ", " << resolution3D[1] << ", " << resolution3D[2] << std::endl
<< "Transform: " << transform << std::endl;
}
// Set the origin of the 2D image
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// For correct (perspective) projection of the 3D volume, the 2D
// image needs to be placed at a certain distance (the source-to-
// isocenter distance {scd} ) from the focal point, and the normal
// from the imaging plane to the focal point needs to be specified.
//
// By default, the imaging plane normal is set by default to the
// center of the 2D image but may be modified from this using the
// command line parameters [image1centerX, image1centerY,
// image2centerX, image2centerY].
double origin2D1[Dimension];
const itk::Vector<double, 3> resolution2D1 = imageReader2D->GetOutput()->GetSpacing();
using ImageRegionType2D = InternalImageType::RegionType;
using SizeType2D = ImageRegionType2D::SizeType;
ImageRegionType2D region2D1 = rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetBufferedRegion();
SizeType2D size2D1 = region2D1.GetSize();
if (!customized_2DCX)
{ // Central axis positions are not given by the user. Use the image centers
// as the central axis position.
image1centerX = ((double)size2D1[0] - 1.) / 2.;
image1centerY = ((double)size2D1[1] - 1.) / 2.;
}
// 2D Image 1
origin2D1[0] = -resolution2D1[0] * image1centerX;
origin2D1[1] = -resolution2D1[1] * image1centerY;
origin2D1[2] = -scd;
imageReader2D->GetOutput()->SetOrigin(origin2D1);
rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->SetOrigin(origin2D1);
registration->SetFixedImageRegion(rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetBufferedRegion());
if (verbose)
{
std::cout << "2D image 1 size: " << size2D1[0] << ", " << size2D1[1] << ", " << size2D1[2] << std::endl
<< " resolution: " << resolution2D1[0] << ", " << resolution2D1[1] << ", " << resolution2D1[2]
<< std::endl
<< " and position: " << origin2D1[0] << ", " << origin2D1[1] << ", " << origin2D1[2] << std::endl;
}
// Initialize the ray cast interpolator
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
// The ray cast interpolator is used to project the 3D volume. It
// does this by casting rays from the (transformed) focal point to
// each (transformed) pixel coordinate in the 2D image.
//
// In addition a threshold may be specified to ensure that only
// intensities greater than a given value contribute to the
// projected volume. This can be used, for instance, to remove soft
// tissue from projections of CT data and force the registration
// to find a match which aligns bony structures in the images.
// 2D Image 1
interpolator1->SetProjectionAngle(dtr * projAngle1);
interpolator1->SetFocalPointToIsocenterDistance(scd);
interpolator1->SetThreshold(threshold);
interpolator1->SetTransform(transform);
interpolator1->Initialize();
registration->SetInitialTransformParameters(transform->GetParameters());
// optimizer->SetMaximize( true ); // for GradientDifferenceTwoImageToOneImageMetric
optimizer->SetMaximize(true); // for NCC
optimizer->SetMaximumIteration(100);
optimizer->SetMaximumLineIteration(4); // for Powell's method
optimizer->SetStepLength(1.0);
optimizer->SetStepTolerance(0.02);
optimizer->SetValueTolerance(0.001);
// The optimizer weightings are set such that one degree equates to
// one millimeter.
itk::Optimizer::ScalesType weightings(transform->GetNumberOfParameters());
weightings[0] = 1. / dtr;
weightings[1] = 1. / dtr;
weightings[2] = 1. / dtr;
weightings[3] = 1.;
weightings[4] = 1.;
weightings[5] = 1.;
optimizer->SetScales(weightings);
if (verbose)
{
optimizer->Print(std::cout);
}
// Create the observers
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
CommandIterationUpdate::Pointer observer = CommandIterationUpdate::New();
optimizer->AddObserver(itk::IterationEvent(), observer);
// Start the registration
// Create a timer to record calculation time.
itk::TimeProbesCollectorBase timer;
if (verbose)
{
std::cout << "Starting the registration now..." << std::endl;
}
try
{
timer.Start("Registration");
// Start the registration.
registration->Update();
timer.Stop("Registration");
}
catch (itk::ExceptionObject& err)
{
std::cout << "ExceptionObject caught !" << std::endl;
std::cout << err << std::endl;
system("pause");
return -1;
}
using ParametersType = RegistrationType::ParametersType;
ParametersType finalParameters = registration->GetLastTransformParameters();
const double RotationAlongX = finalParameters[0] / dtr; // Convert radian to degree
const double RotationAlongY = finalParameters[1] / dtr;
const double RotationAlongZ = finalParameters[2] / dtr;
const double TranslationAlongX = finalParameters[3];
const double TranslationAlongY = finalParameters[4];
const double TranslationAlongZ = finalParameters[5];
const int numberOfIterations = optimizer->GetCurrentIteration();
const double bestValue = optimizer->GetValue();
std::cout << "Result = " << std::endl;
std::cout << " Rotation Along X = " << RotationAlongX << " deg" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Rotation Along Y = " << RotationAlongY << " deg" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Rotation Along Z = " << RotationAlongZ << " deg" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Translation X = " << TranslationAlongX << " mm" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Translation Y = " << TranslationAlongY << " mm" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Translation Z = " << TranslationAlongZ << " mm" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Number Of Iterations = " << numberOfIterations << std::endl;
std::cout << " Metric value = " << bestValue << std::endl;
// Write out the projection images at the registration position
// ~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
TransformType::Pointer finalTransform = TransformType::New();
// The transform is determined by the parameters and the rotation center.
finalTransform->SetParameters(finalParameters);
finalTransform->SetCenter(isocenter);
using ResampleFilterType = itk::ResampleImageFilter<InternalImageType, InternalImageType>;
// The ResampleImageFilter is the driving force for the projection image generation.
ResampleFilterType::Pointer resampleFilter1 = ResampleFilterType::New();
resampleFilter1->SetInput(caster3D->GetOutput()); // Link the 3D volume.
resampleFilter1->SetDefaultPixelValue(0);
// The parameters of interpolator1, such as ProjectionAngle and FocalPointToIsocenterDistance
// have been set before registration. Here we only need to replace the initial
// transform with the final transform.
interpolator1->SetTransform(finalTransform);
interpolator1->Initialize();
resampleFilter1->SetInterpolator(interpolator1);
// The output 2D projection image has the same image size, origin, and the pixel spacing as
// those of the input 2D image.
resampleFilter1->SetSize(rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetLargestPossibleRegion().GetSize());
resampleFilter1->SetOutputOrigin(rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetOrigin());
resampleFilter1->SetOutputSpacing(rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetSpacing());
resampleFilter1->SetOutputDirection(rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetDirection());
resampleFilter1->SetDefaultPixelValue(100);
//// Do the same thing for the output image 2.
//ResampleFilterType::Pointer resampleFilter2 = ResampleFilterType::New();
//resampleFilter2->SetInput(caster3D->GetOutput());
//resampleFilter2->SetDefaultPixelValue(0);
if (debug)
{
InternalImageType::PointType outputorigin2D1 = rescaler2D1->GetOutput()->GetOrigin();
std::cout << "Output image 1 origin: " << outputorigin2D1[0] << ", " << outputorigin2D1[1] << ", "
<< outputorigin2D1[2] << std::endl;
}
flipFilter1->SetInput(resampleFilter1->GetOutput());
// Rescale the intensity of the projection images to 0-255 for output.
using RescaleFilterType = itk::RescaleIntensityImageFilter<InternalImageType, OutputImageType>;
RescaleFilterType::Pointer rescaler1 = RescaleFilterType::New();
rescaler1->SetOutputMinimum(0);
rescaler1->SetOutputMaximum(255);
rescaler1->SetInput(flipFilter1->GetOutput());
using WriterType = itk::ImageFileWriter<OutputImageType>;
WriterType::Pointer writer1 = WriterType::New();
writer1->SetFileName(fileOutput1);
writer1->SetInput(rescaler1->GetOutput());
try
{
std::cout << "Writing image: " << fileOutput1 << std::endl;
writer1->Update();
}
catch (itk::ExceptionObject& err)
{
std::cerr << "ERROR: ExceptionObject caught !" << std::endl;
std::cerr << err << std::endl;
}
timer.Report();
system("pause");
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
fixed picture(DSA picture)
result picture
out_put.tif (333.2 KB)